THE ROLE OF COMPANION PLANTING IN NATURAL PEST CONTROL
Pest control is an age-old problem for farmers and gardeners alike, but using chemicals to eradicate pests can be expensive and harmful to the environment. A more natural way of controlling pests is through companion planting, which involves growing certain plants together to protect each other from unwanted insects. In this article, we’ll look at the role of companion planting in natural pest control and how it can be used to maintain a healthy and productive garden.
Companion planting is a practice that humans have used since the dawn of agriculture. It involves selecting and growing specific plants together in order to exploit their beneficial interactions. This method helps reduce the number of pest problems by providing a natural form of pest control that doesn’t rely on chemical solutions or other artificial means. By understanding how different plants interact, gardeners can choose which crops to plant near each other to maximize their pest-fighting potential.
By combining traditional knowledge with modern science, companion planting offers an effective and sustainable solution to pest problems. Not only does it help protect crops from damage caused by insects, but it also supports biodiversity within the garden ecosystem. In this article, we’ll explore how companion planting works and how it can be used as an effective form of natural pest control for any size garden or farm.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPANION PLANTING
The practice of companion planting involves growing different species of plants together in order to benefit both plants. This can be done in many ways, such as by providing protection from pests, supplying nutrients, or improving soil fertility. For example, when two types of vegetables are planted close together, one may act as a trap crop for pests, while the other may provide necessary nutrients or shade for better growth. By doing this, you protect your crops from damage caused by pests and improve their overall health.
In addition to protecting from pests, companion planting can also help attract beneficial insects that prey on harmful insects. Planting flowers around your garden can attract pollinators and other beneficial insects, which will then feed on any destructive bugs that try to feed on your crops. This helps keep the balance between beneficial and harmful insects in check.
Using companion planting as part of your natural pest control strategy can be an effective way to protect your crops and improve their overall health without using any kind of chemical pesticides or other artificial means. With careful planning and observation, you can create a healthy garden ecosystem where all plants thrive while keeping out unwanted guests.
HOW COMPANION PLANTING WORKS AS A PEST CONTROL STRATEGY
Companion planting is a natural form of pest control that has been used for centuries. It involves strategically planting certain plants together to create an environment that repels or defends against pests. While it is not a foolproof method of pest control, companion planting can be an effective tool in the gardener’s arsenal.
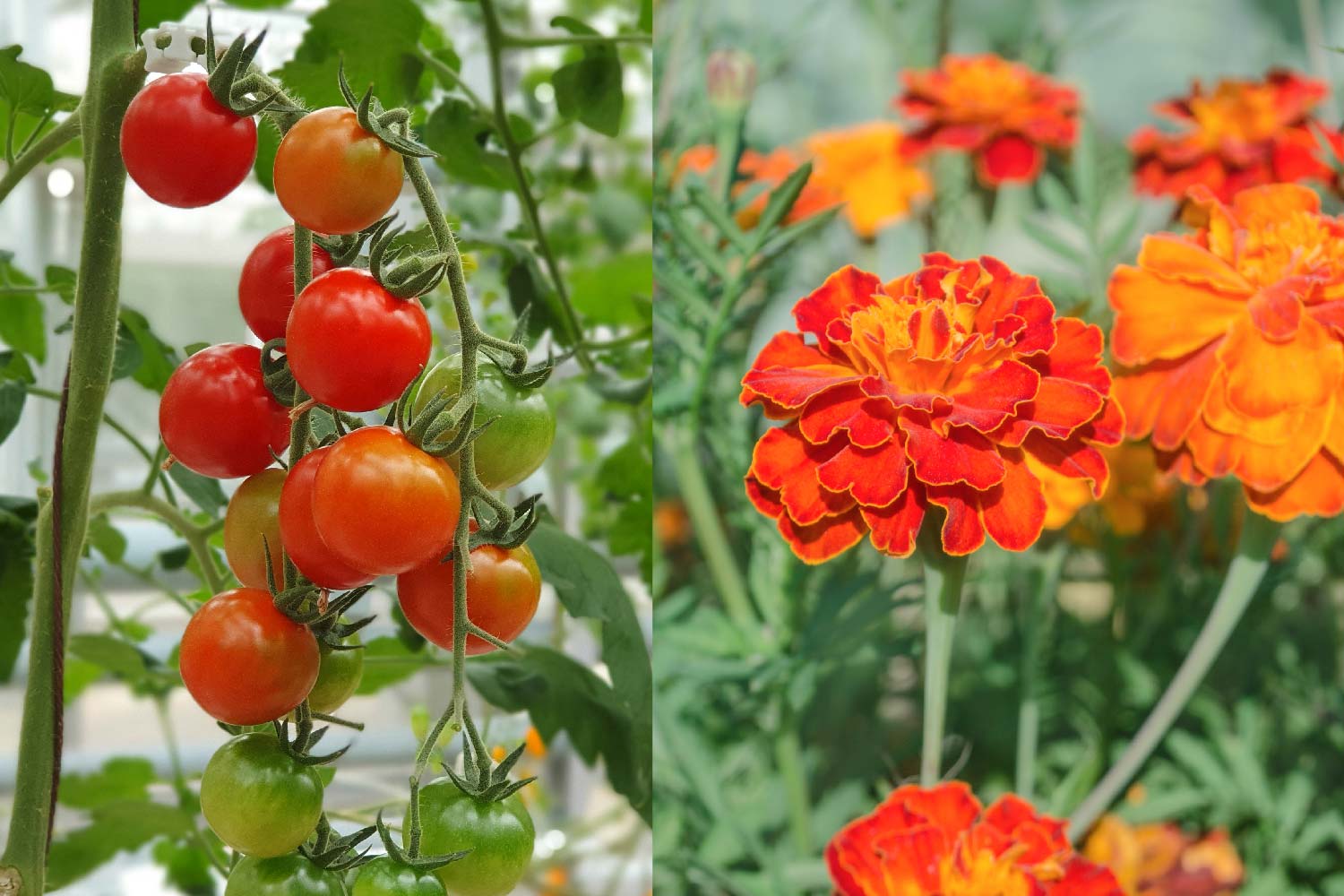
The concept behind companion planting is simple: certain plants have natural insect-repellent properties and can deter or confuse pests when planted near other crops. For example, garlic planted near roses will help ward off aphids, while marigolds planted around tomatoes will help keep away whiteflies. Additionally, some plants attract beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and hoverflies, which will eat the garden pests.
It’s important to remember that companion planting requires knowledge of the particular plants being grown, as well as an understanding of the local climate and soil conditions, to be successful. To get started with companion planting, research what types of plants grow best together in your area and experiment with what works best for your garden.
EXAMPLES OF COMPANION PLANTS AND THE PESTS THEY DETER
One example is the pairing of basil and tomatoes. The strong scent of basil helps to repel a variety of common garden pests, such as aphids, flies, and tomato hornworms. Not only does this help protect the tomato crop, but it also improves the flavor of the tomatoes due to increased nutrient uptake. Additionally, basil releases a compound called cineole into the soil, which helps to increase the vigor and productivity of tomatoes growing nearby.
Another example is marigolds planted alongside squash or cucumbers. Marigolds have a very powerful scent that deters squash bugs and cucumber beetles. Furthermore, they contain pyrethrum, an organic insecticide that can provide additional protection for vulnerable crops like squash or cucumbers. Finally, marigold roots secrete a substance called alpha-terthienyl which helps to improve soil fertility and promote better root development in neighboring plants!
When used appropriately, these companion plantings provide multiple benefits for gardeners looking for natural pest control solutions without relying on potentially hazardous chemicals. They are easy to implement and effectively keep pests away from valuable crops while improving their overall health and productivity.
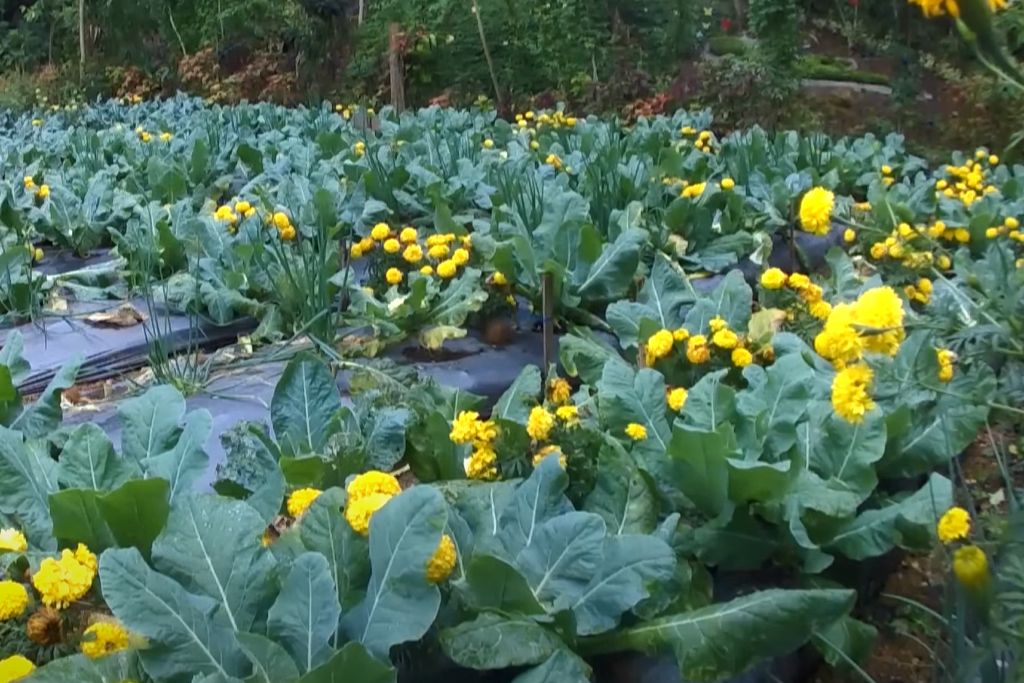

COMMON MISCONCEPTIONS ABOUT COMPANION PLANTING
A common misconception is that companion planting requires much extra work and effort. While it’s true that this type of pest control requires more attention than chemical-based solutions, it doesn’t need to be overly laborious. With careful planning and research, companion planting can be an effective way to protect your garden from pests with minimal effort involved.
Another misconception is that companion plants must be grown together to be effective against pests. However, while they should be planted in close proximity for maximum effectiveness, they don’t necessarily need to grow side-by-side. In fact, if the companion plants are too close together, they may compete for resources such as light or water, which can reduce their overall effectiveness at controlling pests.
It’s also important to remember that companion plants aren’t always a silver bullet for pest control. While certain combinations of plants may help deter certain types of bugs, other insects may still find their way into the garden regardless of the presence of companions. To ensure the best possible results when using companion planting for pest control, it’s important to make sure you have identified the correct combination of plants and locations before getting started.
BEST PRACTICES FOR INCORPORATING COMPANION PLANTING INTO YOUR GARDEN
Companion planting is an effective and sustainable way to protect your garden from pests. When used correctly, companion planting can significantly reduce the number of pesticides needed to keep your plants healthy. However, it’s important to remember that there are best practices for incorporating companion planting into your garden.
First, research what companion plants work best together. Different plants have different preferences regarding their neighbors, so you’ll want to make sure they’re compatible with each other. You should also consider the size and growth rate of each plant. Some may grow too quickly or overtake others if not kept in check.
Finally, plan how you will rotate your companion crops throughout the growing season. Rotating crops helps balance the nutrients in the soil and keeps pests away by denying them a consistent food source in one area of your garden. You’ll want to give each species enough space and time to thrive before moving on to another crop rotation cycle.
By following these best practices for companion planting, you can give your garden a better chance at success without relying heavily on toxic chemicals.
THE ROLE OF SOIL HEALTH IN NATURAL PEST CONTROL AND COMPANION PLANTIN
Soil health is an integral component of sustainable gardening and natural pest control. The soil quality can directly impact how well companion plants work to repel pests, making it an essential factor when creating a companion planting plan.
Quality soil can be achieved through organic composting and mulching, which help to boost fertility and improve the texture of the soil. This can help support beneficial insects that prey on harmful pests and the growth of companion plants. Additionally, healthy soils are better able to absorb moisture, reducing water loss and improving plant survival rates.
However, it’s important to maintain balance in the garden ecosystem–too much fertilization can also lead to excessive insect populations. To avoid this, gardeners should opt for natural fertilizers like manure or fish emulsion when supplementing nutrients in their soil. This will help keep the soil balanced and promote healthier root systems in both companion plants and vegetables alike.
TIP: Keep your garden healthy by monitoring your soil’s nutrient levels regularly! This will allow you to adjust your fertilizer application accordingly so you can reap all the benefits of companion planting without damaging your garden’s delicate ecosystem.
COMMON MISTAKES TO AVOID WHEN USING COMPANION PLANTING FOR PEST CONTROL
- Planting too much of one companion plant: While companion plants can effectively deter pests, planting too much of one type can attract other pests or create an imbalance in your garden ecosystem. Be sure to plant a variety of companion plants to maintain balance.
- Planting incompatible plants together: Some plants have chemical compounds that can negatively affect the growth and health of other plants. Be sure to research the compatibility of plants before planting them together as companion plants.
- Ignoring soil health: Soil health plays a crucial role in the success of companion planting. Neglecting soil health can lead to poor plant growth, nutrient deficiencies, and an increased risk of pests and disease.
- Not rotating companion plants: Planting the same companion plants in the same location year after year can lead to a build-up of pests and diseases. Rotate your companion plants to keep your garden healthy and balanced.
- Planting at the wrong time: Timing is important for companion planting. Planting too early or too late can affect the effectiveness of companion plants in deterring pests.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What Is The Cost Of Companion Planting For Pest Control?
The cost of companion planting for pest control varies depending on the type of plants used and the size of the garden. Generally speaking. However, most companion plants are relatively inexpensive since they are usually native species or varieties that are easy to find in local nurseries. Additionally, many companion plants offer other benefits, such as attracting pollinators or providing food for beneficial insects like ladybugs. Here’s a list of some common companion plants that can help with pest control:
- Marigolds: Repel nematodes
- Nasturtiums: Repel aphids
- Catnip: Repels ants and fleas
- Basil: Repels mosquitoes and flies
- Garlic: Repels Japanese beetles
As you can see, companion planting is not only a great way to naturally control pests, but also to add diversity to your garden without breaking the bank. It can also provide other benefits such as increasing yields or attracting beneficial insects that will help keep your garden healthy. All in all, using companion planting for pest control can be an excellent choice when you want good results without spending too much money.
Is Companion Planting Suitable For Indoor Gardening?
Companion planting is an age-old gardening technique which uses the natural tendencies of plants to benefit each other. Employing this method can help to naturally control pests and create a healthier garden environment. But is it suitable for indoor gardening?
The answer is yes, companion planting can be used in indoor gardens as well as outdoor ones. The same principles apply: by planting certain plants together, you can create a beneficial relationship which helps to deter pests. For example, marigolds are known to repel certain insects, so they may be planted with vegetables or other susceptible plants as a form of defense. Basil is also thought to have pest-repelling qualities, so it could be planted near lettuces or tomatoes to keep those pesky bugs away.
Using companion planting in an indoor garden may require some experimentation and research on your part. It’s important to think about what types of plants will work best together and how they will interact with one another in that particular environment. With the right combination of plants and a bit of patience, you can successfully use companion planting indoors to keep pests from ruining your harvest.
CONCLUSION
To summarize, companion planting can be a great way to reduce the cost of pest control and protect your garden. It’s important to remember that companion planting can take some time to be effective against pests, so patience is key. The most common companion plant used for pest control is marigolds, but many other plants can also be used. Additionally, companion planting is suitable for indoor gardening and can help protect against disease-carrying pests.
Overall, companion planting is an effective method for natural pest control that doesn’t require chemicals or expensive products. It’s also relatively easy to do; anyone with a bit of knowledge about plants can start using this technique in their gardens. Not only does it offer protection against pests, but it also helps create a healthier ecosystem and a more sustainable environment.
In conclusion, companion planting is an excellent way to naturally protect your garden from pests while promoting a healthier environment. With its low cost and ease of implementation, it’s no wonder why more and more gardeners are turning to this pest control method!